Pension Funds: Key Players in the Global Farmland Grab
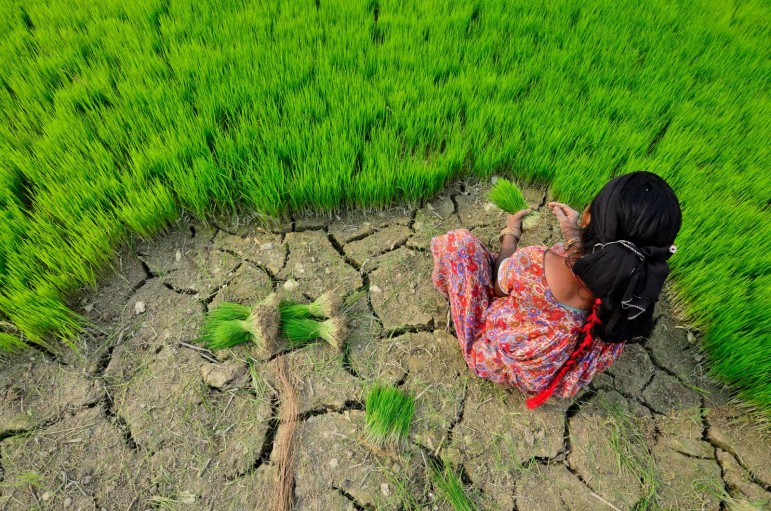
Large scale agricultural land acquisitions are generating conflicts and controversies around the world. A growing body of reports show that these projects are bad for local communities and that they promote the wrong kind of agriculture for a world in the grips of serious food and environmental crises. 1 Yet funds continue to flow to overseas farmland like iron to a magnet. Why? Because of the financial returns. And some of the biggest players looking to profit from farmland are pension funds, with billions of dollars invested.
Pension funds currently juggle US$23 trillion in assets, of which some US$100 billion are believed to be invested in commodities. Of this money in commodities, some US$5–15 billion are reportedly going into farmland acquisitions. By 2015, these commodity and farmland investments are expected to double.
Pension funds are supposed to be working for workers, helping to keep their retirement savings safe until a later date. For this reason alone, there should be a level of public or other accountability involved when it comes to investment strategies and decisions. In other words, pension funds may be one of the few classes of land grabbers that people can pull the plug on, by sheer virtue of the fact that it is their money. This makes pension funds a particularly important target for action by social movements, labour groups and citizens’ organisations.

The size & weight of pensions
Today, people’s pensions are often managed by private companies on behalf of unions, governments, individuals or employers. These companies are responsible for safeguarding and “growing” people’s pension savings, so that these can be paid out to workers in monthly cheques after they retire. Anyone lucky enough both to have a job and to be able to squirrel away some income for retirement probably has a pension being administered by one firm or another. Globally, this is big money. Pension funds are currently juggling US$23 trillion in assets. 2 The biggest pension funds in the world are those held by governments, such as Japan, Norway, the Netherlands, Korea and the US (see Table 1).
Table 1: World’s top 20 pension funds (2010)
|
Rank |
Fund |
Country |
Total assets (US$ millions) |
| 1 | Government Pension Investment | Japan |
1,315,071 |
| 2 | Government Pension Fund–Global | Norway |
475,859 |
| 3 | ABP | Netherlands |
299,873 |
| 4 | National Pension | Korea |
234,946 |
| 5 | Federal Retirement Thrift | US |
234,404 |
| 6 | California Public Employees | US |
198,765 |
| 7 | Local Government Officials | Japan |
164510 |
| 8 | California State Teachers | US |
130,461 |
| 9 | New York State Common | US |
125,692 |
| 10 | PFZW (now PGGM) | Netherlands |
123,390 |
| 11 | Central Provident Fund | Singapore |
122,497 |
| 12 | Canada Pension | Canada |
122,067 |
| 13 | Florida State Board | US |
114,663 |
| 14 | National Social Security | China |
113,716 |
| 15 | Pension Fund Association | Japan |
113,364 |
| 16 | ATP | Denmark |
111,887 |
| 17 | New York City Retirement | US |
111,669 |
| 18 | GEPF | South Africa |
110,976 |
| 19 | Employees Provident Fund | Malaysia |
109,002 |
| 20 | General Motors | US |
99,200 |
Source: Pensions & Investments, 6 September 2010, P&I/Towers Watson World 300